8.1 Million People Now Work in Renewables, New Study Finds
More than 8.1 million people worldwide are now employed by the renewable energy industry – a 5% increase from last year – according to a report released today by IRENA at its 11th Council meeting.
The report, Renewable Energy and Jobs – Annual Review 2016, also provides a global estimate of the number of jobs supported by large hydropower, with a conservative estimate of an additional 1.3 million direct jobs worldwide.
IRENA’s Director-General Adnan Z. Amin noted today that this growth is significant given that it stands in contrast to trends across the broader energy sector; the total number of renewable energy jobs worldwide rose in 2015 while jobs in the broader energy sector fell. In the US for example, renewable energy jobs increased 6% while employment in oil and gas decreased 18%. Likewise in China, renewable energy employed 3.5 million people, while oil and gas employed 2.6 million.
“This increase is being driven by declining renewable energy technology costs and enabling policy frameworks. We expect this trend to continue as the business case for renewables strengthens and as countries move to achieve their climate targets agreed in Paris.” – IRENA Director-General Adnan Z. Amin
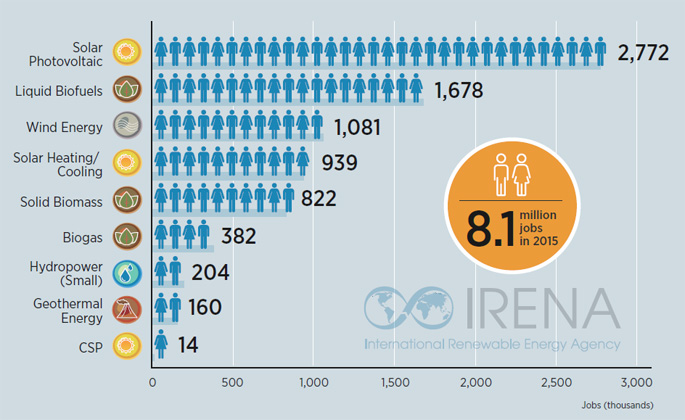
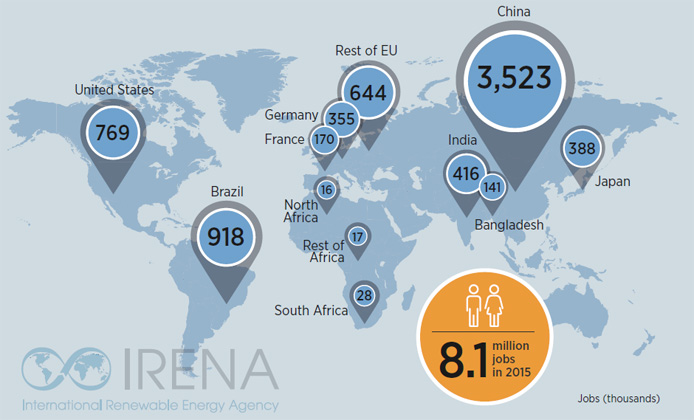
Countries with the most renewable energy jobs in 2015 included China, Brazil, the US, India, Japan and Germany. The solar photovoltaic (PV) sector remains the largest renewable energy employer worldwide with 2.8 million jobs (up from 2.5 at last count) with jobs in manufacturing, installation and operations & maintenance. Liquid biofuels was the second largest global employer with 1.7 million jobs, followed by wind power, which grew 5 per cent to reach 1.1 million global jobs.
Select report findings:
- Solar PV is the largest renewable energy employer with 2.8 million jobs worldwide, an 11% increase from last count.
- Strong wind installation rates in China, the US and Germany drove a 5% increase in global employment to reach 1.1 million jobs. Wind employment in the US alone rose by 21%.
- Jobs in liquid biofuels, solar heating and cooling, and large and small hydropower decreased due to various factors including increased mechanisation, slowing housing markets, the removal of subsidies and the drop in new installations.
- With more than a third of the global renewable energy capacity additions in 2015, China led employment with 3.5 million jobs.
- In the EU, the UK, Germany and Denmark were the global leaders in offshore wind employment. Overall, job figures in the EU declined for the fourth year due to weak economic growth. Germany remains the highest EU renewables employer– employing nearly as many as France, the UK, and Italy combined.
- In the US, renewable energy employment increased 6% driven by growth in wind and solar. Solar employment grew 22% – 12 times faster than job creation in the US economy – surpassing jobs in oil and gas. Employment in wind industry grew 21%.
- Japan experienced impressive gains in solar PV in recent years, resulting in a 28% increase in employment in 2014.
- In India, solar and wind markets have seen substantial activity, as the ambitious renewable energy targets are translated into concrete policy frameworks.
- Africa has seen many developments leading to job creation, including solar and wind development in Egypt, Morocco, Kenya and South Africa.
- IRENA’s early research indicates that the renewable energy sector employed larger shares of women than the broader energy sector.
Download Renewable Energy and Jobs – Annual Review 2016